Learn Together
Suggested Time: 65 minutes
Reading: Product Market Fit (10 mins)
What is a product?
A product is how you deliver value to your organization’s customers
What is a market?
A market is a broader group of potential customers, defined by ranges. A customer is the person you’ve identified as most likely to purchase your products
What is PMF?
Product Market Fit (PMF) is the point where a product or service offered by a company perfectly meets the needs and wants of its target customers. In other words, PMF is when the product or service is in high demand and customers are satisfied with its features, benefits, and overall value. It is the stage where a business has found the right product-market match, where the product solves a real problem for the target market and meets their expectations.
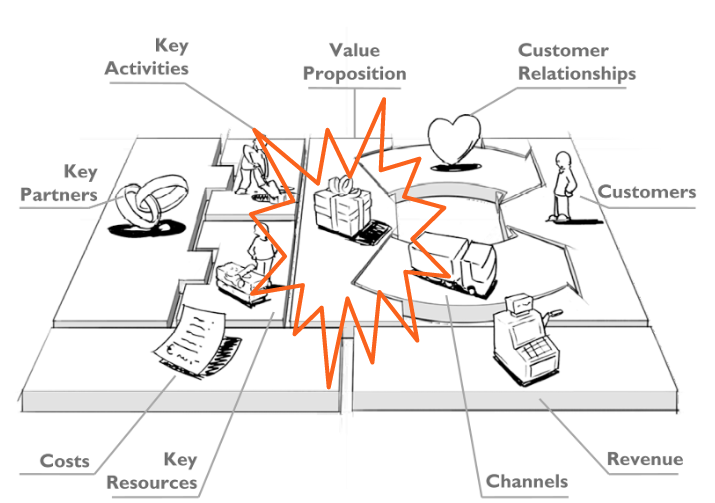
Defining Value Proposition
The Value Proposition is the worth that you offer to your customers. It’s typically a paragraph or sentence that articulates what your services, business or organization does, who it brings value to, and why it’s valuable to those people. It should be clear why someone would choose you over another company.
When defining Value Proposition, consider the ** experiences** of your customers and the capability of your product or service to help customers minimize pains and maximize gains.
Ask Yourself:
- What products and services are we offering to help them complete their jobs?
- Jobs are the functional, emotional, social jobs your customers need to have done
- Is what you’re offering a pain reliever?
- Pains identify blockages and problems your customers may face trying to get the jobs done
- Is what you’re offering a gain creator?
- Gains describe positive outcomes the customer expects when the job is getting done
Steps to Define Value Proposition:
- Identify Pain relievers, Gain Creators and Key Features
- What is the resulting Minimum Viable Product?
- Propose experiments to test your value proposition
- Determine what constitutes a pass/fail signal
- Talk to at least 5-10 potential customers
- Update Value Proposition Canvas w/ Changes
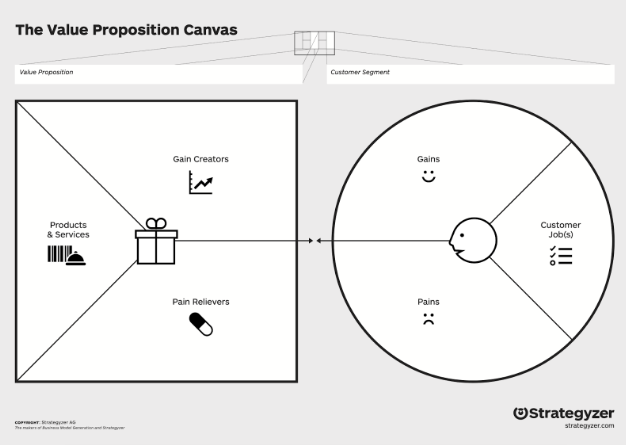
Activity: Defining your Value Proposition (10 mins)
Take ten minutes to free-write responses to the following questions.
The 5 W’s of your Customer:
Work with customers to identify your target market. The goal is to learn from potential customers to take an idea and turn it into a solution. Ask:
- Where and when they experience their problem?
- Why do they experience the problem and others don’t?
- How are different people experiencing the problem differently?
Identifying the Context:
- What is your competition?
- Why is this problem so hard to solve? (Ask customers!)
- How big is this problem?
- How do you fix it?
Identifying the Pain Killers:
Reduce or eliminate wasted time, costs, negative emotions, and risks.
How does your product perform in the following areas?
- Saving time, money, and effort
- Making customers feel better
- Fixing solutions that underperform
TIP: Rank the pains that your product addresses according to intensity and frequency for your customer. If it happens once a year, it may not be a significant bother, but if it is happening daily, it has a more intense impact.
Identifying the Gain Creators:
What are the benefits the customer wants, desires or expects?
- Saving time and money
- Provides better quality
- Outperforms competitors’ products
- Makes life easier
- Creates positive consequences (more sales for a business)
TIP: Rank the gains that your product or service creates according to relevance. Is this a substantial or insignificant gain creator, and how frequently does it occur?
Reading: What is the minimum viable product? (10 mins)
A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is the most basic version of a product or service that a company can offer to its target customers to test the demand before investing significant time and resources in the development of a fully-featured product.
The MVP usually includes only the essential features and functionality needed to solve a specific problem or fulfill a particular need for the target market. The goal of an MVP is to quickly and inexpensively test the market, get feedback from early adopters, and make adjustments based on the insights gained. By starting with an MVP, companies can minimize risk, avoid building unnecessary features, and focus on what is truly important for their customers. As the product evolves, additional features and functionality can be added based on customer feedback and market demand.
The purpose of the MVP is to test the ability of a product to meet minimal customer need.
Step One: Identify the value proposition for your business
- Problem statement: What is the problem?
- Technology/Market insight: Why is the problem so hard to solve?
- Market size: How big is the problem?
- Competition: What do customers do today?
- Product: How do you do it?
Step Two: Define Your Minimum Value Product
Use the following prompts to help you think through the steps to bringing your MVP to your customer base.
To test a physical minimum viable product, the first step is to create a prototype or a sample version of the product. This helps in testing your understanding of the problem you are trying to solve, which in turn helps you understand the solution better. By doing this, you can prove that the product solves a core problem for customers. As you continue to test the product, you will learn the minimum set of features that are required to satisfy your customers. This can be done through various means such as interviews, demos, and prototypes. During these interactions, it is important to make lots of eye contact to ensure that you are receiving valuable feedback and insights from your customers.
To test a web/mobile minimum viable product, start with a “low fidelity” version of the web or app. This can be done through the use of wireframes or PowerPoint presentations with mockups. By doing this, you can receive valuable feedback from your customers, which in turn helps validate your business model and ensures that you are addressing a real problem. As you move forward, you can create a “high fidelity” version of the product with more features and a concrete layout. This version helps test your understanding of the solution and proves that it solves a core problem for customers. Take into account the feedback from early adopters (or “earlyvangelists”) who are willing to take a risk on your startup’s product or service because they can envision its potential to solve a critical and immediate problem. This approach helps to avoid building products that nobody wants and maximizes the learning per time spent on the development process.
Step Three: Test the Minimum Viable Product
Create a broad plan for testing your Minimum Viable Product by thinking through the following tactics. \
- Conduct user testing: Get feedback from potential customers by inviting them to test the MVP and provide feedback. Observe how they use the product and ask for their opinions on its features, design, and usability.
- Use A/B testing: Create two versions of the MVP, and test them with different groups of users to see which version performs better. A/B testing can help you identify which features or design elements are more effective.
- Run a beta test: Invite a small group of users to test the MVP in a real-world environment. Collect feedback and make improvements based on their experiences.
- Create a landing page: Create a simple landing page that describes the MVP and its features. Use online advertising (such as AdWords) or social media to drive traffic to the landing page and see how many users sign up for more information or express interest in the product.
- Conduct market research: Research your target market to understand their needs and preferences. Use surveys or focus groups to get feedback on the MVP and identify potential areas for improvement.
- Measure key metrics: Identify the key metrics that will determine the success of the MVP, such as user engagement, retention, or conversion rates. Measure these metrics over time to see how the product is performing and make adjustments as necessary.
Remember that the purpose of testing an MVP is to validate your assumptions and learn from user feedback. Use the insights gained from testing to refine the product and create a better experience for your customers.
Reading: Market Research (10 mins)
Market research is the process of gathering information about a target market to make informed business decisions. To conduct market research, first, define the research goals and the target market. Next, choose the appropriate research methods, such as surveys, interviews, or secondary research. Design the research instruments, such as survey questions or interview questions, to elicit the desired information. Collect the data and analyze it to draw conclusions and identify trends in the market. Use the insights gained from the research to inform business decisions and improve products or services.
Market Definition Cheatsheet:
- Category: What category of products does the customer put you in?
- Who: Who is the target audience within the category? There are always multiple personas within a single category, so this breaks it down further.
- Problems: What problems does your target audience have related to the category?
- Motivations: What are the motivations behind those problems? Why are those problems important to your target audience?
How to Build a Remarkable Product:
- Have a great idea.
- Talk to customers. Develop a market thesis.
- Listen to their problems, not their solutions.
- Initiate rapid prototyping and user testing.
- Build the solution to their problems.
- Test the solution with them.
- Did it work? If not, go back to Step 2 and repeat.
- By the time you make it to this step, you’ve likely gone through this list ~30 times!
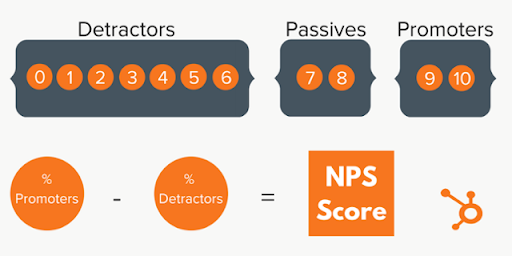
What is a Net Promoter Score?
A Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a metric used by businesses to measure customer loyalty and satisfaction with a product, service or brand. It is calculated by asking customers a single question: “How likely are you to recommend this product/service/brand to a friend or colleague?” The answer is given on a scale of 0-10, with 0 being “not at all likely” and 10 being “extremely likely.”
Based on their response, customers are grouped into three categories: promoters (score 9-10), passives (score 7-8), and detractors (score 0-6). The NPS is then calculated by subtracting the percentage of detractors from the percentage of promoters. The score can range from -100 to 100, with a higher score indicating greater customer loyalty and satisfaction.
How do I know when I have a Product Market Fit?
- You consistently get an NPS > 50
- Returning customers who refer their friends, coworkers, family, etc.
- Sign-ups to subscriptions, loyalty programs, etc. and/or showing up to engagements
Breakout Rooms (15 mins)
Meet in small groups to revisit the progress you’ve made on your vision and mission statement since last week.