Learn Together
Suggested time: 75 mins
Reading (10 mins)
Let’s revisit our earlier concept of Product-Market-Fit by considering this quote from Andy Rachleff, a business hall of famer:
“If you address a market that really wants your product – if the dogs are eating the dog food – then you can screw up almost everything in the company and you will succeed. Conversely, if you’re really good at execution but the dogs don’t want to eat the dog food, you have no chance of winning.”
Creating a strong Go-To-Market strategy ensures that your company is creating a product (here, dog food) that is too good for your customers (here, dogs) to resist. So, in short: PMF = find the dogs, make the dog food, let them eat!

What is a Go-to-Market strategy?
A Go-to-Market (GTM) strategy is a plan that outlines how a company will introduce and sell its products or services to its target market. It includes all the outside resources (such as sales force and distributors) that the company will use to deliver their unique value proposition and achieve a competitive advantage. The end goal of this strategy is to enhance the overall customer experience by offering a superior product and/or more competitive pricing.
Some key definitions for understanding GTM:
- A product is how you deliver value to your organization’s customers.
- A market is a more broad group of potential customers, defined by ranges.
- A customer is the person you’ve identified as most likely to purchase your products.
The GTM strategy should also define the pricing, packaging, and positioning of the product or service, as well as the metrics and KPIs to measure success and track progress towards the goals.
The ultimate goal of a GTM strategy is to create a sustainable and profitable business by acquiring and retaining customers, building brand recognition and loyalty, and delivering value that meets or exceeds the expectations of the target market.
Sales vs. Marketing
Let’s compare some key difference between sales and marketing:
Sales:
- All activities that lead to the selling of goods or services
- Sales works directly with prospects to reinforce the value of the company’s solution to convert prospects into customers
- The primary focus of sales is to hit quotas and sales volume goals
- Sales has a short-term focus than marketing
Marketing:
- Describes all activities that help spark interest in your business
- Marketing informs and attracts leads and prospects to your company and product or service
- The primary goal of marketing is to look at the big picture and promote the company, product or service, and brand
- Marketing departments are responsible for pricing the products and communicating how the product fills the customers’ needs and wants
Keep in mind that in early-stage businesses (like yours), everyone is doing sales.
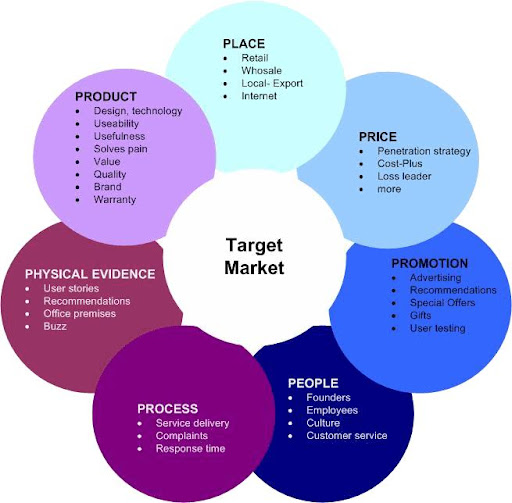
The following graphic illustrates the 7 P’s of a target market:
Business Structure
There are several types of business structures, each with its own legal and tax implications, ownership structure, and level of complexity. Here are some of the most common types:
- Sole proprietorship: A business owned and operated by a single person. The owner is personally responsible for all aspects of the business, including its debts and liabilities.
- Partnership: A business owned and operated by two or more people who share the profits and losses of the business. Partners can be personally liable for the debts and liabilities of the partnership.
- Limited liability company (LLC): A flexible business structure that provides limited liability protection for the owners (called members) while allowing them to participate in the management of the business. An LLC can be taxed as a partnership or a corporation.
- Corporation: A legal entity that is separate from its owners (called shareholders) and provides limited liability protection for them. Corporations can issue stocks and raise capital from investors.
- Cooperative: A business owned and operated by a group of individuals or organizations who share the profits and benefits. Cooperatives can be formed in various industries, including agriculture, retail, and housing.
- Non-profit: An organization that operates for a charitable, educational, or social purpose and is exempt from paying taxes. Non-profits can be structured as a corporation, LLC, or other legal entity.
Choosing the right business structure depends on various factors, including the type of business, the number of owners, the level of risk, the tax implications, and the desired level of control and flexibility. It is important to consult with a legal and tax professional before making a decision.
Founder Interview (32 mins)
Nami Baral - Startup Business Plans
Reading: Business Registration (10 mins)
Registering a business involves completing the legal requirements for the formation of a new business entity, including registering with the appropriate government agencies and obtaining necessary permits and licenses. Here are the general steps to register a business:
- Choose a business name: Choose a unique and distinctive name that reflects the nature of your business and is not already in use by another business.
- Determine the business structure: Choose a legal structure that best fits your business, such as sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, or corporation.
- Register with the government: Register your business with the appropriate government agencies at the federal, state, and local levels. This may include obtaining an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS, registering for state and local taxes, and obtaining any necessary permits and licenses.
- Open a business bank account: Open a separate bank account for your business to keep your personal and business finances separate.
- Obtain insurance: Obtain insurance to protect your business from liability and other risks.
- Create business contracts: Create contracts and agreements for your business, such as a partnership agreement or a customer contract.
The registration process can vary depending on the location and type of business. It is recommended to consult with a legal and tax professional to ensure compliance with all legal and regulatory requirements.
Read and Discuss (10 mins)
Take a moment to read this case study about MeUndies.
As a group, ask and answer one another’s questions you have about this material.